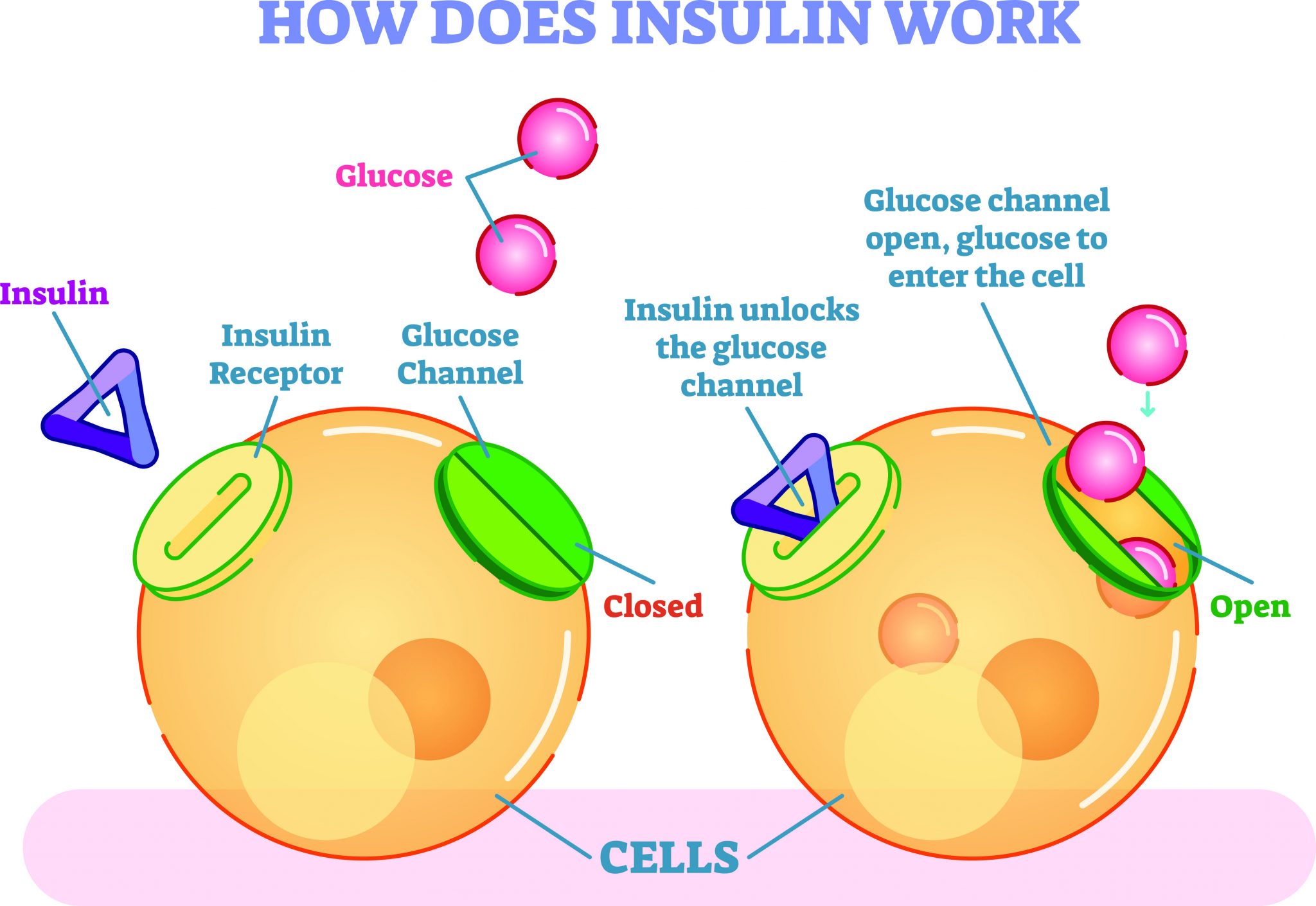
Sugar Cell Function . “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12 o 6. Sugars have the general chemical formula ch 2. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every. Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway,. Sugars are commonly attached to proteins in a process called glycosylation. Glucose is central to energy consumption. Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or other functional group. Sugars, and glucose in particular, are important molecules for cells because they are the primary energy source. It is found in fruits and honey and is the major.
from bloodglucosevalue.com
Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every. Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway,. Sugars are commonly attached to proteins in a process called glycosylation. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12 o 6. It is found in fruits and honey and is the major. Glucose is central to energy consumption. Sugars, and glucose in particular, are important molecules for cells because they are the primary energy source. Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or other functional group. Sugars have the general chemical formula ch 2.
Blood Glucose Control
Sugar Cell Function Glucose is central to energy consumption. Sugars have the general chemical formula ch 2. Sugars, and glucose in particular, are important molecules for cells because they are the primary energy source. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every. Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or other functional group. Glucose is central to energy consumption. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12 o 6. Sugars are commonly attached to proteins in a process called glycosylation. Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway,. It is found in fruits and honey and is the major.
From www.clevalab.com
The Basic Principles of a Cell Sugar Cell Function Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every. Sugars, and glucose in particular, are important molecules for cells because they are the primary energy source. Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or other functional group. Sugars are commonly attached to proteins in a process called glycosylation. Glucose is central to energy consumption. It is found in fruits and honey and. Sugar Cell Function.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Impact of Dietary Sugars on βCell Function Sugar Cell Function Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every. Sugars have the general chemical formula ch 2. Sugars, and glucose in particular, are important molecules for cells because they are the primary energy source. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12 o 6. Sugars are commonly attached to proteins in a process called glycosylation. It is found in fruits and. Sugar Cell Function.
From www.nih.gov
Sugars on Cell Surface Are Key to Flu Infections National Institutes Sugar Cell Function Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway,. Sugars are commonly attached to proteins in a process called glycosylation. Sugars have the general chemical formula ch 2. Sugars, and glucose in particular, are important molecules for cells because they are the primary energy source. Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or other functional group. It is found in fruits and honey. Sugar Cell Function.
From mednexus.org
Glucose Metabolism and Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection Sugar Cell Function Sugars, and glucose in particular, are important molecules for cells because they are the primary energy source. Glucose is central to energy consumption. Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway,. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12 o 6. Sugars have the general chemical formula ch 2. It is found in fruits and honey and is the major. Typically. Sugar Cell Function.
From www.mdpi.com
Cells Free FullText Emerging Roles of SWEET Sugar Transporters in Sugar Cell Function Sugars, and glucose in particular, are important molecules for cells because they are the primary energy source. Glucose is central to energy consumption. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12 o 6. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every. Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway,. Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or other functional group. Sugars have. Sugar Cell Function.
From healthjade.com
What and How Your Body Metabolises Sugar Glucose and Fructose Sugar Cell Function Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or other functional group. Sugars are commonly attached to proteins in a process called glycosylation. Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway,. Sugars have the general chemical formula ch 2. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12 o 6. Glucose is central to energy consumption. It is found in fruits and honey. Sugar Cell Function.
From gettinghealthier.com
Glucose Getting Healthier Sugar Cell Function Sugars have the general chemical formula ch 2. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12 o 6. Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or other functional group. Sugars, and glucose in particular, are important molecules for cells because they are the primary energy source. Glucose is central to energy consumption. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every.. Sugar Cell Function.
From www.inverse.com
What Is the Human How Scientists Unlocked the Sugar Code Inverse Sugar Cell Function It is found in fruits and honey and is the major. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every. Glucose is central to energy consumption. Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or other functional group. Sugars, and glucose in particular, are important molecules for cells because they are the primary energy source. Sugars are commonly attached to proteins in a. Sugar Cell Function.
From cen.acs.org
Potential diabetes therapy Engineered cells that control blood sugar Sugar Cell Function Sugars are commonly attached to proteins in a process called glycosylation. It is found in fruits and honey and is the major. Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway,. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12 o 6. Glucose is central to energy consumption. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every. Sugars, and glucose in particular, are important molecules. Sugar Cell Function.
From www.researchgate.net
Model of intracellular distribution of plant sugar transporters. Three Sugar Cell Function Sugars have the general chemical formula ch 2. Sugars are commonly attached to proteins in a process called glycosylation. Glucose is central to energy consumption. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12 o 6. Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or other functional group. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every. It is found in fruits and. Sugar Cell Function.
From www.breathewellbeing.in
Role of Insulin and How Insulin Works to Maintain Your Glucose Levels Sugar Cell Function Sugars, and glucose in particular, are important molecules for cells because they are the primary energy source. Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or other functional group. Sugars are commonly attached to proteins in a process called glycosylation. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12 o 6. Glucose is central. Sugar Cell Function.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
The Endocrine Pancreas Anatomy and Physiology II Sugar Cell Function Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12 o 6. Sugars have the general chemical formula ch 2. Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway,. Sugars are commonly attached to proteins in a process called glycosylation. Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or other functional group. Glucose is central to energy consumption.. Sugar Cell Function.
From www.universityofcalifornia.edu
Cracking the sugar code Why the is the next big thing in Sugar Cell Function Sugars have the general chemical formula ch 2. Sugars are commonly attached to proteins in a process called glycosylation. It is found in fruits and honey and is the major. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12 o 6. Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway,. Typically the attachment is to a. Sugar Cell Function.
From www.biologyonline.com
Glucose Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary Sugar Cell Function Sugars are commonly attached to proteins in a process called glycosylation. Sugars, and glucose in particular, are important molecules for cells because they are the primary energy source. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every. Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway,. Sugars have the general chemical formula ch 2. Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or other functional group.. Sugar Cell Function.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT The chemistry of life PowerPoint Presentation ID6348408 Sugar Cell Function Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway,. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12 o 6. Sugars are commonly attached to proteins in a process called glycosylation. Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or other functional group. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every. Sugars, and glucose in particular, are important molecules for cells because they are the. Sugar Cell Function.
From www.frontiersin.org
Frontiers Plant Fructokinases Evolutionary, Developmental, and Sugar Cell Function Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway,. Sugars have the general chemical formula ch 2. Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or other functional group. Sugars are commonly attached to proteins in a process called glycosylation. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every. Glucose is central to energy consumption. It is found in fruits and honey and is the major.. Sugar Cell Function.
From www.frontiersin.org
Frontiers Origins and History of the Minimal Model of Glucose Regulation Sugar Cell Function Glucose is central to energy consumption. It is found in fruits and honey and is the major. Sugars have the general chemical formula ch 2. Sugars, and glucose in particular, are important molecules for cells because they are the primary energy source. Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or other functional group. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every.. Sugar Cell Function.
From www.researchgate.net
Molecular components of sugar signaling networks and their involvement Sugar Cell Function Sugars, and glucose in particular, are important molecules for cells because they are the primary energy source. “sweet”) has the molecular formula c 6 h 12 o 6. Carbohydrates are ubiquitous energy sources for every. It is found in fruits and honey and is the major. Glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway,. Typically the attachment is to a hydroxyl or. Sugar Cell Function.